The Cyber Extended Project Qualification
(The CyberEPQ).
Brought to you by CIISec
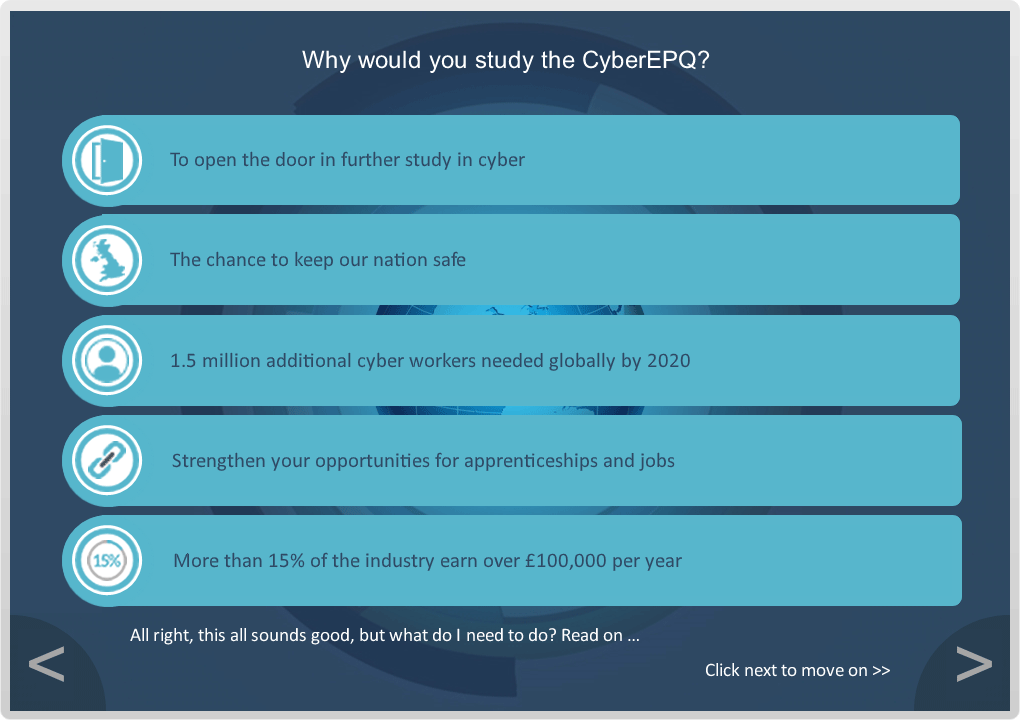
Break into a Cyber Security career with the CyberEPQ.
This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site, you are agreeing to our use of cookies.
Brought to you by CIISec
Break into a Cyber Security career with the CyberEPQ.
The CyberEPQ is the UK’s first and only Extended Project Qualification (EPQ) in Cyber Security. This unique Cyber Security qualification has been developed by a consortium of education and Cyber Security partners to help provide a starting point for anyone considering a career in Cyber Security; to go to university, start an apprenticeship or change career.
The Cyber EPQ qualification is delivered online using distance learning tools with its content guided by the National Occupational Standards (NOS), and aligned with the Chartered Institute of Information Security (CIISec) and the Cyber Security Body of Knowledge (CyBOK) Skills and Knowledge Framework.
The EPQ is a Level 3 qualification, accredited by City & Guilds, worth up to an extra 28 UCAS points. The course is delivered using a distance learning platform (the Moodle) and can be studied through your school or independently. School Learners are supervised by their teachers and Independent Learners will have a supervisor assigned to them.
Everybody. There are no formal entry requirements for studying the course, it is open to everyone. It is recommended that you have studied at Level Two (GCSE level or equivalent) prior to the course. You must be 14 years old or above on enrolment.
The CyberEPQ was designed to bridge the gap in Cyber Security qualifications between GCSE Computer Studies and a degree in Cyber Security. It also assists in training potential Cyber Security professionals and those who are looking for a change in career into Cyber Security.
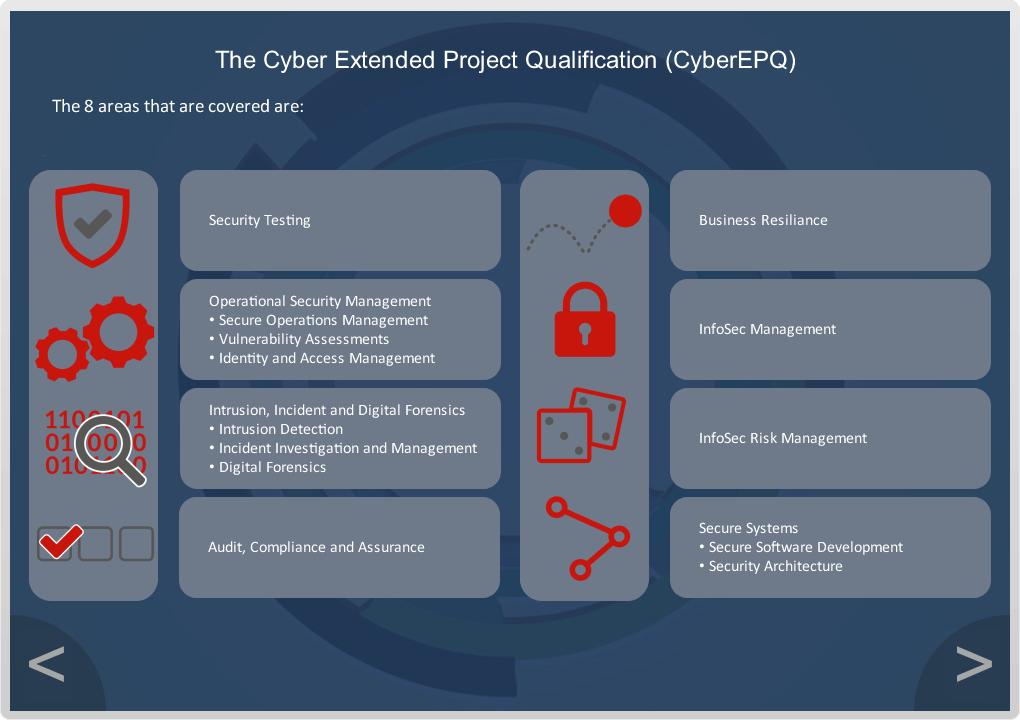
The course includes 10 Core Compulsory Modules and 3 Specialist Modules. At least one of the specialist modules must be completed.
In this module, you will be introduced to the topic of Cyber Security, including a brief history of ethical hacking, Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability (the CIA Triad) of data as well as the Computer Misuse Act.
Take a look at computing from the breaking of the Enigma code at Bletchley Park, the world’s first programmable computer - Colossus, through to the development of mainframes, personal computers, and the development of the internet.
Explore the study of the techniques of secret writing, especially code and cipher systems, methods as well as the procedures, processes, methods of making and using secret writing, as codes or ciphers.
In addition, you will get the chance to reflect on the next big thing in cyber security, namely Quantum Computing. You will get the opportunity to consider whether quantum computing is a challenge to current cryptographic practices.
In this module you will explore Cybercrime, which is used to describe two closely linked, but distinct ranges of criminal activity, namely cyber dependent crimes, and cyber-enabled crimes. Cyber-dependent crimes, can be committed only through the use of Information and Communications Technology (‘ICT’) devices, where the devices are both the tool for committing the crime, and the target of the crime. Whereas Cyber-enabled crimes refer to traditional crimes which can be increased in scale or reach by the use of computers, computer networks or other forms of ICT.
This module looks at Risk Management, which is the process of identifying, assessing, and controlling threats to an organisation's capital and earnings. These threats, or risks, could stem from a wide variety of sources, including financial uncertainty, legal liabilities, strategic management errors, accidents, and natural disasters.
IT security threats and data-related risks, and the risk management strategies to alleviate them, have become a top priority for digitized companies. As a result, a risk management plan increasingly includes companies' processes for identifying and controlling threats to its digital assets, including proprietary corporate data, a customer's personally identifiable information (PII) and intellectual property.
Governance refers to the actions, processes, traditions, and institutions by which authority is exercised and decisions are taken and implemented. Risk governance applies the principles of good governance to the identification, assessment, management, and communication of risks
Furthermore, we have added a section on the Ethics of cyber security practice. You shall be examining how ethics are critical to any sound cybersecurity defence strategy.
Explore Security Testing, which is a type of Software Testing that uncovers vulnerabilities, threats, and risks in a software application, and prevents malicious attacks from intruders. The purpose of Security Tests is to identify all possible loopholes and weaknesses of the software system which might result in a loss of information, revenue, or reputation at the hands of employers or outsiders of the organisation. The main goal of Security Testing is to identify the threats in the system and measure its potential vulnerabilities, so the threats can be encountered, and the system does not stop functioning or cannot be exploited. It also helps in detecting all possible security risks in the system and helps developers to fix the problems through coding.
In this module you will also learn about Vulnerability Assessment which is a risk management process used to identify, quantify, and rank possible vulnerabilities to threats in a given system. It is not isolated to a single field and is applied to systems across different industries such as; IT systems; Energy and other Utility systems; Transportation; Communication Systems.
Explore Digital Forensics, which is the process by which information is extracted from data storage media (e.g., devices, remote storage and systems associated with computing, imaging, image comparison, video processing and enhancement [including CCTV], audio analysis, satellite navigation, communications), rendered into a useable form, processed, and interpreted to obtain intelligence for use in investigations, or evidence for use in criminal proceedings.
In this module you will look at Incident Response Management, which is an organised strategy for addressing and managing the after effects of a security breach or cyber-attack, also known as an incident involving IT, computer incident or security. The purpose is to control the situation in a way that limits harm and reduces the time and cost of recovery.
This module explores Identity and Access Management (IAM), which is a collective term that covers products, processes, and policies used to manage user identities and regulate user access within an organisation.
This module also looks at authentication, authorisation, and accountability (AAA) which refers to a common security framework for mediating network and application access. AAA intelligently controls access to computer resources by enforcing strict access and auditing policies. This process ensures that access to network and software application resources can be restricted to specific, legitimate users.
Explore Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). AI makes it possible for machines to learn from their experiences, adjusting to new inputs and performing human-like tasks. Most AI applications rely heavily on deep learning and natural language processing, which is referred to in general as Machine Learning. Cyber security experts are looking into the potential for AI and ML to identify and counteract sophisticated cyber-attacks with minimal human intervention.
Also study GDPR which is designed to ensure that the integrity of any personal data that is collected, managed, stored, or processed by an organisation is fully protected. It brings new mandatory requirements for data controllers and processors. These provide further safeguards, ranging from the need to gain an individual’s consent to store and use their data - and their right to know what personal data is held about them - right through to the need for some companies to appoint data protection officers.
GDPR also introduces much heavier penalties for breaches of the regulation by companies that fail to comply. The onus is on individual firms to understand the risks associated with any personal data they hold or use and to take the necessary measures to mitigate those risks.
Within this module you will also get to investigate how the UK enacted the GDPR into law as the Data Protection Act 2018 (GDPR 2018).
Explore Audit Compliance functions which are meant to reasonably ensure that the company is complying with all applicable laws, rules, and regulations, as well as internal codes of conduct, policies, and procedures. The Internal Audit function is designed to monitor and evaluate the company’s internal control environment as to its adequacy, efficiency, and effectiveness.
Security assurance can be defined as the confidence that a system meets its security requirements and is resilient against security vulnerabilities and failures. The confidence indicated by the security assurance represents the level of trust we give to a system that is safe to use.
In this module, discover how human factors of cyber security represent the actions or events when human error results in a successful hack or data breach. Sharing of passwords, poor patch management, double-clicking on unsafe URLs, and organizational access through a personal device are just a few human errors that lead to a security threat, many of which could be mitigated.
You will also explore how by defining the anti-requirements or abuse frames which make explicit potential adversarial behaviour of attackers and design mechanisms, they can protect an organisation. Security is not a zero-sum game, meaning the gain of the attacker does not equal the loss of the defender. Therefore, understanding the goals, assets, and risks for the organisation is not enough. It is important to understand the goals of potential attackers and the gain they may achieve by having access to the organisation’s assets.
Examine Penetration Testing (pen-testing or pentesting) which is a method of testing, measuring, and enhancing established security measures on information systems and support areas.
In this way organisations can gain assurance in the security of an IT system by attempting to breach some or all of that system's security, using the same tools and techniques as an adversary might.
Penetration testing should be viewed as a method for gaining assurance in an organisation's vulnerability assessment and management processes, not as a primary method for identifying vulnerabilities.
In this module, you will learn about Software Security. This is an idea implemented to protect software against malicious attack and other hacker risks so that the software continues to function correctly under such potential risks.
Security is necessary to provide integrity, authentication, and availability. Software systems can be attacked to steal information, monitor content, introduce vulnerabilities, and damage the behaviour of software.
Look at security architecture which refers to a set of security principles, methods and models designed to align to a company’s objectives and help keep the organisation safe from cyber threats. Security architecture translates the business requirements to executable security requirements.
Modern businesses need to have a robust security architecture framework to protect their most important information assets. The strengthening of security architecture will close common weaknesses which can drastically reduce the risk of an attacker succeeding in breaching a company’s systems.
“We were looking for a course that would actually be relevant to the changing world of employment particularly for our computing students and when I came across the CyberEPQ I thought it’s a perfect course that would allow them to develop independent study skills as well as actually becoming more au fait and knowledgeable about the sector as it were.”
“What it does give you is a starter, a very broad understanding about what is in the cyber discipline and what cyber security is all about”
“For a future career, I think the CyberEPQ is fantastic because she has been exposed to so many people, the networking opportunities have been fabulous and that will go on. But as a girl, in particular, it has given her confidence to feel that she can be in this industry, she doesn’t have to be intimidated by it”
“It really really is something that focused your mind on potential career paths. And in terms of the doors that are opened for these students, it’s just absolutely fantastic”
“I think that (the CyberEPQ) is a really good way to be able to enable young people to learn the skills to be able to give them a real grounding and good foundations to get into Cyber Security”
£200
Still have questions? Request a call back
£550
Still have questions? Request a call back
You can pre-register for the academic year 2024-25 online. Enrolment will open on Tuesday 18th June 2024.
Your data will only be used by CIISec to send you relevant news. Your data will never be shared with third parties unless you provide your consent for us to do so. Your data will be held securely and monitored under EU data protection law. You may unsubscribe at any time using the options provided in-email or by proactively contacting our administration team at [email protected]
© Chartered Institute of Information Security. Privacy Policy Refund Policy Site by Dgtl